UBC ARC Sockeye Tutorial
A comprehensive guide to using UBC's Advanced Research Computing Sockeye cluster
Introduction
Welcome to this tutorial on the UBC Advanced Research Computing (ARC) Sockeye High-Performance Computing (HPC) system. This guide is designed to help researchers and students navigate the powerful Sockeye cluster, which was updated to use the SLURM scheduling system on October 31, 2024.
In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through the process of setting up and running a simple deep neural network training job on the Sockeye cluster. This hands-on approach will give you practical experience with the system and prepare you for more complex computational tasks.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- A valid UBC Campus-Wide Login (CWL)
- An active UBC ARC Sockeye Account
If you don’t have these, please contact the UBC IT department or visit the UBC ARC website for information on how to obtain access.
Cluster Structure
Understanding the structure of the Sockeye cluster is crucial for efficient usage. Let’s take a look at its architecture:
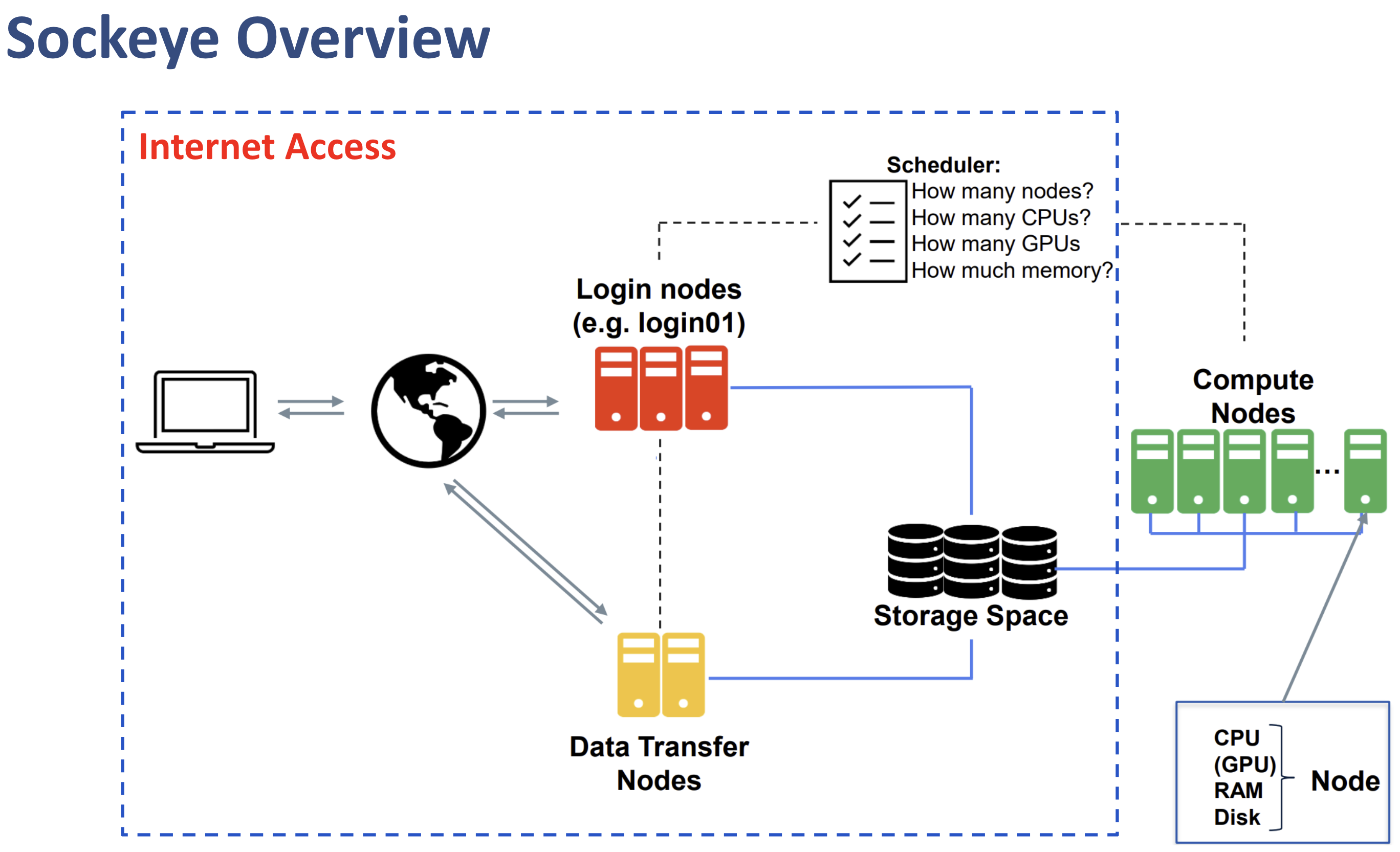
The Sockeye cluster consists of:
- Login Nodes: These are your entry points to the cluster. You’ll use these to manage files, submit jobs, and monitor your work.
- Compute Nodes: These powerful machines perform the actual computations. They’re organized into different partitions based on their capabilities (e.g., GPU nodes, high-memory nodes).
- Storage Systems: Including home directories, scratch space for temporary files, and project storage for shared data.
Submitting a Job
Now, let’s get hands-on with submitting a job to the Sockeye cluster. We’ll use a simple deep neural network training script as an example.
Step 1: Prepare Your Environment
First, ensure you’re in the correct directory:
cd scripts/jobs
Step 2: Submit the Job
To submit your job to the SLURM scheduler, use the following command:
sbatch train.sh
This command sends your train.sh script to the job queue. SLURM will allocate resources and run your job when they become available.
Step 3: Monitor Your Job
You can check the status of your job using:
squeue -u $USER
Important Note
Warning: The current job script contains an intentional error. This is designed as an exercise for you to practice debugging in an HPC environment. Try to identify and fix the error before the job actually runs!
Tips for Success
- Resource Estimation: Carefully estimate the resources (CPU, GPU, memory, time) your job needs to avoid over- or under-allocation.
- Use Modules: Familiarize yourself with the module system to load necessary software and libraries.
- Data Management: Use scratch space for temporary files and transfer only necessary data to compute nodes.
- Job Arrays: For parameter sweeps or multiple similar jobs, consider using SLURM job arrays.
Further Resources
We hope this tutorial helps you get started with the UBC ARC Sockeye cluster. Happy computing!